In today’s digitally driven world, Google has become synonymous with the internet itself. With its vast index of web pages and an unparalleled ability to deliver relevant search results, Google has revolutionized the way we access and navigate information. But have you ever wondered about the minds behind this extraordinary creation? In this article, we delve into the fascinating history of Google’s inception, shedding light on the individuals whose ingenuity and perseverance birthed this technological titan.

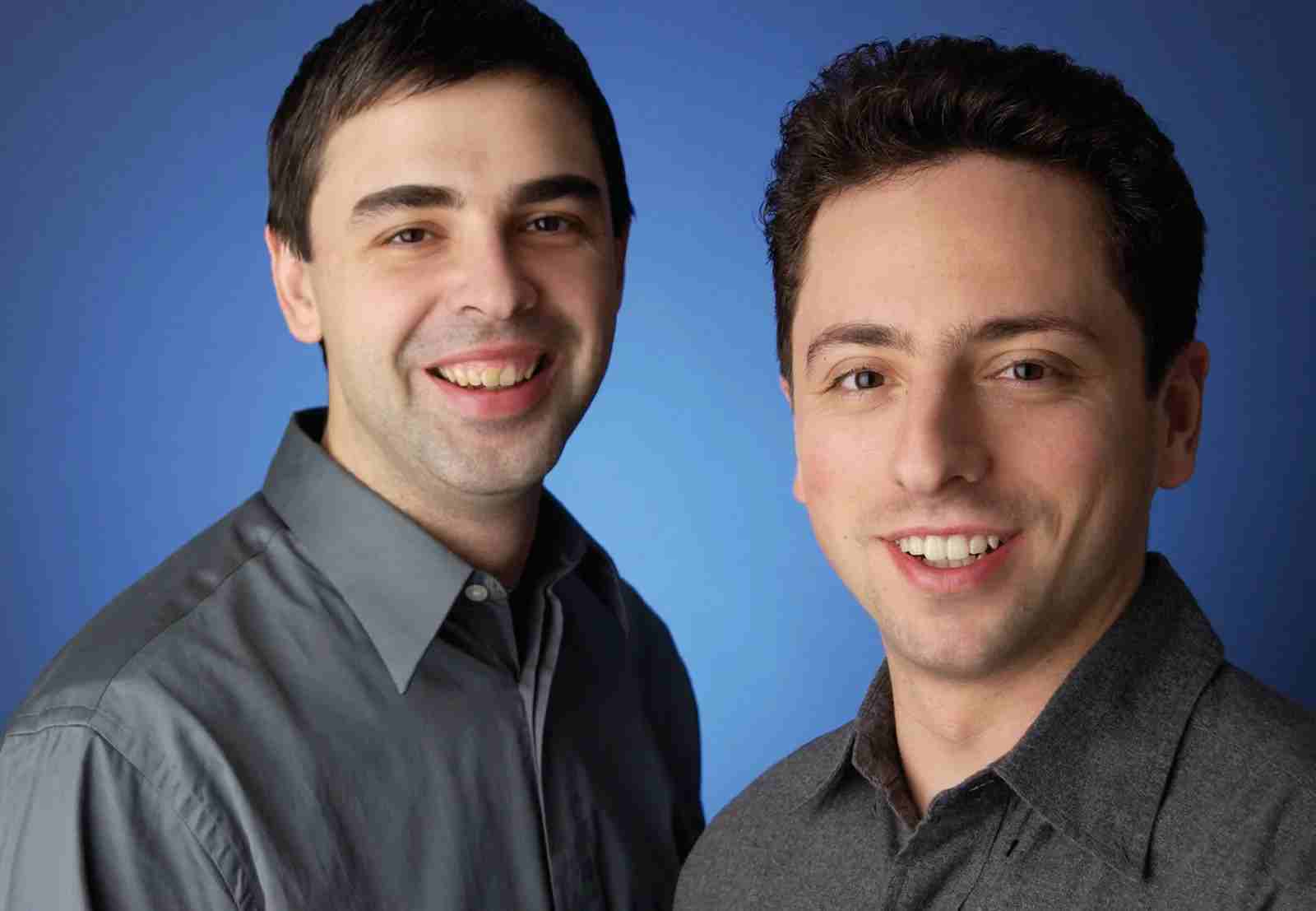
The story of Google can be traced back to the hallowed halls of Stanford University, where two Ph.D. students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, crossed paths. Brin, a native of Moscow, Russia, and Page, a young computer science enthusiast, shared a common interest in the vast potential of the internet.
Their collaboration began in 1995 when Page arrived at Stanford, and the duo started working together on a project that aimed to enhance internet search capabilities. The foundation for what would later become Google was laid when Brin and Page developed a search algorithm called “Backrub,” which analyzed the relationships between web pages to determine their relevance.
The groundbreaking nature of Backrub prompted Page and Brin to expand their project beyond a mere research endeavor. In 1998, they incorporated their invention as a company named Google Inc., a name inspired by the mathematical term “googol,” which refers to the number one followed by a hundred zeros. This choice reflected their vision to organize the vast amount of information available on the internet.
As Google gained traction, it quickly outgrew its humble origins. In 1999, Andy Bechtolsheim, a co-founder of Sun Microsystems, recognized the potential of Google and made a pivotal investment of $100,000 in the company. This funding allowed Page and Brin to take Google to the next level and establish their headquarters in Mountain View, California, commonly known as the Silicon Valley.
Over the years, Google expanded its offerings beyond search, introducing innovative products and services that shaped the digital landscape. Key developments included the introduction of Google AdWords in 2000, a platform that revolutionized online advertising, and the launch of Google Maps in 2005, which transformed the way we navigate and explore the world.
In 2004, Google made its initial public offering (IPO), and Larry Page assumed the role of CEO, while Sergey Brin took on the position of President. The company’s rapid growth and success attracted top talent from around the globe, establishing Google as an industry leader.
Under the leadership of Page and Brin, Google continued to innovate and expand its influence across various industries. In 2006, they acquired YouTube, the world’s largest video-sharing platform, cementing Google’s dominance in the online video space. Additionally, Google launched Android, an open-source mobile operating system, in collaboration with the Open Handset Alliance in 2007, revolutionizing the smartphone industry.
In recent years, Google has ventured into artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, developing products such as Google Assistant and Google Home. Furthermore, the company has made significant investments in renewable energy, pledging to operate entirely on carbon-free energy by 2030.
Backrub, PageRank, and Delivering Search Results:

Google’s search engine is synonymous with efficiency and accuracy, providing users with a wealth of information at their fingertips. Behind this remarkable capability lies a sophisticated algorithm called PageRank, which revolutionized the way search results are ranked and delivered.
Backrub: The Precursor to PageRank:
The seeds of Google’s success were sown in the late 1990s when Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two Ph.D. students at Stanford University, developed an innovative search engine algorithm known as Backrub. This algorithm aimed to improve upon the existing methods of web page ranking by considering the interconnectedness of pages across the internet.
The Birth of PageRank:
Building upon the foundation of Backrub, Page and Brin refined and expanded their algorithm, ultimately giving birth to PageRank. Named after Larry Page, this revolutionary approach to ranking web pages focused on assessing the importance and relevance of pages based on the number and quality of links pointing to them.
PageRank analyzed the complex web of links on the internet, considering each link as a vote of confidence for the destination page. The algorithm assigned a numerical value, or PageRank score, to each page, with higher scores indicating greater significance. This novel approach allowed Google to deliver search results that were not only comprehensive but also highly relevant to users’ queries.
Google’s commitment to providing the most accurate and useful search results led to continuous refinements of the PageRank algorithm. One notable addition was the integration of anchor text, the clickable text within a hyperlink, as a factor in ranking. By analyzing anchor text, Google could gain insights into the context and relevance of linked pages, further enhancing the precision of search results.
Google’s emphasis on delivering relevant search results propelled it to the forefront of the search engine industry. In 1998, Page and Brin incorporated their project as Google Inc., with a mission to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful. Their dedication to innovation and accuracy soon garnered attention and user loyalty.
As Google’s user base grew exponentially, the company invested in expanding its infrastructure and improving its algorithms. By deploying a vast network of data centers across the globe, Google was able to handle the increasing volume of search queries while maintaining speed and efficiency.
While PageRank remained the cornerstone of Google’s search engine, the company continuously refined and introduced new algorithms to improve the user experience. In 2003, Google launched Fresno, an algorithm update that aimed to provide more up-to-date search results by indexing the web more frequently.
In subsequent years, Google introduced several major updates to its search algorithm, such as Panda (2011) and Hummingbird (2013), which emphasized quality content and semantic search, respectively. These updates focused on understanding the context and intent behind search queries, enabling Google to deliver more accurate and contextually relevant results.
Google’s commitment to delivering the most comprehensive and relevant search results has transformed it into the world’s most dominant search engine. With billions of search queries processed daily, Google continues to refine its algorithms and explore new frontiers such as voice search and mobile optimization.
Larry Page and Google:

Larry Page, the co-founder of Google, is an iconic figure in the technology industry. His visionary leadership and relentless pursuit of innovation have transformed Google from a modest search engine project into a global technology powerhouse.
Larry Page’s story begins at Stanford University, where he pursued a Ph.D. in computer science. It was during his time at Stanford that he crossed paths with Sergey Brin, and together, they embarked on a journey that would change the face of the internet.
The Birth of Google:
In 1998, Page and Brin incorporated their invention, initially known as Backrub, as a company named Google Inc.. Inspired by the mathematical term “googol,” representing a one followed by a hundred zeros, the name reflected their audacious mission to organize and make accessible the vast amount of information on the internet.
Central to Google’s success is the development of PageRank, an algorithm that revolutionized web page ranking and search engine functionality. Larry Page played a pivotal role in creating and refining PageRank, which analyzes the interconnectedness of web pages to determine their relevance and importance.
Under Page’s leadership, Google rapidly expanded its influence and diversified its offerings. In 2000, the company launched Google AdWords, a game-changing advertising platform that revolutionized online marketing. AdWords introduced a pay-per-click model, allowing businesses to target their ads based on relevant search queries.
In 2004, Google went public with an initial public offering (IPO), marking a significant milestone in the company’s growth. Page assumed the role of CEO while maintaining an active role in shaping Google’s strategic direction.
Page’s vision extended beyond search, and he actively pursued groundbreaking innovations and strategic acquisitions. Google’s acquisition of YouTube in 2006 solidified its position in the online video domain, making it the largest video-sharing platform globally.
Page also championed the development of Android, an open-source mobile operating system that revolutionized the smartphone industry. This strategic move allowed Google to expand its reach and influence in the mobile ecosystem.
Larry Page’s leadership was characterized by a relentless pursuit of ambitious projects. He established Google X, the company’s secretive research division dedicated to developing “moonshot” projects such as self-driving cars (Waymo) and Project Loon, which aimed to provide internet connectivity to remote areas using high-altitude balloons.
In 2015, Page oversaw a major corporate restructuring, establishing Alphabet Inc. as the parent company of Google and its various subsidiaries. This move allowed Page to focus on overarching strategic initiatives while empowering leaders to run Google’s core operations.
Beyond technology, Larry Page has demonstrated a deep commitment to environmental sustainability. He has been a vocal advocate for renewable energy and has invested in numerous clean energy initiatives. Google itself has made significant strides towards becoming carbon neutral and operates on renewable energy for its data centers.
Sergey Brin and Google: The Innovator Who Transformed the Digital Frontier

Sergey Brin, the co-founder of Google, is a pioneering figure in the technology industry. With his visionary mindset and passion for innovation, Brin played a pivotal role in shaping Google’s trajectory, propelling it to become one of the most influential companies in the world.
Born in Moscow, Sergey Brin migrated to the United States with his family at a young age. It was at Stanford University where Brin’s path intersected with that of Larry Page, forming a partnership that would change the course of internet history.
In 1998, Brin and Page co-founded Google Inc., a company born out of their search engine project known as Backrub. Inspired by the immense potential of organizing and making information accessible, Brin and Page aimed to create a search engine that would revolutionize the way people navigate the web.
The Breakthrough: PageRank and Algorithmic Innovation:
At the heart of Google’s success lies the groundbreaking algorithm called PageRank, developed by Brin and Page. PageRank analyzed the interconnectedness of web pages, considering incoming links as votes of relevance and importance. This algorithm propelled Google’s search engine to deliver more accurate and meaningful search results, setting it apart from its competitors.
As Google grew in prominence, Brin played an instrumental role in expanding the company’s horizons. In 2000, Google launched Google AdWords, an advertising platform that revolutionized the online advertising industry. AdWords introduced a pay-per-click model that allowed businesses to target their ads based on specific search queries.
Brin also championed innovation in other areas, such as Google Books, a project aimed at digitizing and making books searchable online. This initiative aimed to democratize access to knowledge on a global scale.
With the rise of mobile devices, Brin recognized the importance of adapting Google’s services to the mobile platform. Under his guidance, Google developed Android, an open-source mobile operating system that became the foundation for a diverse range of smartphones and applications.
Furthermore, Brin pushed for the development of cloud-based services, leading to the introduction of Google Drive, a cloud storage and collaboration platform. This innovation allowed users to store, access, and share files seamlessly across multiple devices.
Brin’s innovation-driven mindset extended beyond Google’s core operations. He established Google X, a division dedicated to pursuing ambitious projects often referred to as “moonshots.” Notable examples include Google Glass, an augmented reality headset, and Project Loon, an initiative to provide internet connectivity to remote areas using high-altitude balloons.
Alongside his passion for technology, Brin has actively engaged in philanthropy. Through the establishment of the Brin Wojcicki Foundation, he has supported various causes, including medical research and education, to make a positive impact on society.
Who Runs Google Now?
The Founders and Alphabet Inc.:
Larry Page and Sergey Brin, the brilliant minds who co-founded Google, played instrumental roles in shaping the company’s early years. However, as of 2015, Google underwent a corporate restructuring, establishing Alphabet Inc. as the parent company. This restructuring allowed for more focused leadership within various subsidiaries, including Google.
The CEO: Sundar Pichai:

Since 2015, Sundar Pichai has served as the CEO of Google, leading the company’s core operations. Pichai, an Indian-born executive, joined Google in 2004 and played a significant role in the development of various key products, including Google Chrome and Android. Under his leadership, Google has continued to expand its reach and influence across a wide range of technologies and services.
Working alongside Sundar Pichai, Google’s leadership team comprises several key individuals responsible for driving the company’s strategic initiatives.
- Ruth Porat – As the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) of Alphabet Inc., Porat oversees the financial operations and fiscal planning of Google and its subsidiaries.
- Kent Walker – Serving as Google’s Senior Vice President for Global Affairs, Walker focuses on managing legal and policy issues, including privacy and intellectual property matters.
- Hiroshi Lockheimer – In his role as Senior Vice President for Platforms and Ecosystems, Lockheimer is responsible for the development and management of Google’s platforms, including Android and Chrome OS.
- Philipp Schindler – As the Chief Business Officer, Schindler leads Google’s global business operations, focusing on revenue growth, partnerships, and advertising.
- Prabhakar Raghavan – Raghavan serves as Google’s Senior Vice President of Search and leads the team responsible for enhancing Google’s search engine capabilities and user experience.
Within Google, there is a strong emphasis on pursuing ambitious projects referred to as “moonshots” that push the boundaries of technological innovation. These projects are overseen by X, formerly known as Google X, the company’s research and development division. While specific individuals may vary based on project requirements, Astro Teller serves as the Captain of Moonshots, leading the team in exploring breakthrough ideas and technologies.
Beyond the leadership team, Google’s culture is heavily influenced by its co-founders and their vision. The company embraces a culture of innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to making a positive impact on society. Google’s campus, located in Mountain View, California, is known for its vibrant and creative work environment that fosters ingenuity and encourages employees to think outside the box.
The Birth of YouTube: The Global Video-Sharing Phenomenon

The Founders and the Garage Days:
The story of YouTube begins in 2005, when three former PayPal employees, Chad Hurley, Steve Chen, and Jawed Karim, joined forces to create a platform that would enable people to share and discover videos online. Working out of a small office and later a garage in San Mateo, California, they embarked on a journey that would revolutionize the way we engage with visual content.
On April 23, 2005, Jawed Karim uploaded the first video to YouTube, titled “Me at the zoo.” This simple clip marked the humble beginnings of a platform that would go on to host billions of videos from users around the world. However, the road to success was not without its challenges.
One of the key factors that set YouTube apart was its focus on user-generated content. Unlike traditional media platforms, YouTube allowed anyone with an internet connection and a camera to share their videos with a global audience. This democratization of content creation and distribution gave rise to a diverse range of voices and perspectives.
Furthermore, YouTube’s commitment to accessibility played a crucial role in its widespread adoption. The platform supported a wide variety of video formats, making it easy for users to upload and view videos across different devices and internet speeds.
Google’s Acquisition and Global Expansion:
In 2006, YouTube caught the attention of Google, the search engine giant. Recognizing the platform’s immense potential, Google acquired YouTube for $1.65 billion. This acquisition provided YouTube with the resources and infrastructure to further expand its reach and enhance its services.
Under Google’s umbrella, YouTube underwent significant improvements, including the introduction of high-definition (HD) videos, live streaming capabilities, and the implementation of content identification and copyright protection systems.
YouTube’s influence on popular culture and media cannot be overstated. The platform has served as a launchpad for numerous viral videos, internet memes, and influential creators. It has also empowered individuals and grassroots movements to share their stories and advocate for social change on a global scale.
In addition to its cultural impact, YouTube has also become a lucrative platform for content creators. The introduction of YouTube Partner Program enabled creators to monetize their channels through advertisements and sponsorships. This opened up new avenues for individuals to turn their passions into profitable careers, fostering a thriving creator economy.
Income of Google:

Advertising Dominance: The Primary Source of Income:
The primary driver of Google’s income is its advertising business, which generates the majority of its revenue. With its powerful search engine and expansive advertising network, Google offers advertisers a platform to reach a vast audience through targeted advertisements.
Google Ads (previously known as Google AdWords) is the flagship advertising platform, where businesses bid on keywords to display ads alongside search results and on partner websites. This pay-per-click (PPC) model ensures that advertisers only pay when their ads are clicked, making it an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
While advertising remains the cornerstone of Google’s income, the company has strategically diversified its revenue streams to minimize dependence on a single source. Let’s explore some key components:
- Google Cloud: Google’s cloud computing division, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offers a wide range of services, including infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS). GCP competes with other major cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, generating significant revenue for Google.
- YouTube: Acquired by Google in 2006, YouTube has become a major revenue generator through various advertising models, including pre-roll, mid-roll, and display ads. YouTube also offers subscription-based services, such as YouTube Premium and YouTube TV, contributing to its overall income.
- Google Play: Google’s digital distribution platform, Google Play, allows users to download and purchase apps, games, music, movies, and books. The revenue generated from app sales, in-app purchases, and subscriptions contributes to Google’s income.
- Hardware: Google’s hardware division produces a range of consumer electronics, including Pixel smartphones, Nest smart home devices, and Chromebook laptops. Sales of hardware products contribute to Google’s revenue, although it is not as significant as other revenue streams.
- Other Bets: Under the umbrella of Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, there are several subsidiary companies referred to as “Other Bets.” These ventures, such as Waymo (autonomous vehicles) and Verily (life sciences and healthcare), although not major revenue contributors currently, have the potential for future growth and innovation.
Google’s financial performance and income are disclosed through comprehensive financial reports issued by Alphabet Inc., its parent company. These reports provide detailed insights into the company’s revenue, operating income, net income, and other key financial metrics. They also allow investors, stakeholders, and the general public to evaluate Google’s financial health and growth trajectory.
Fast Facts About Google:

Key Milestones:
- 1998: Larry Page and Sergey Brin incorporated their invention as Google Inc. in Mountain View, California.
- 2000: Google introduced Google AdWords, a pay-per-click advertising platform that transformed online marketing.
- 2004: Google went public with an initial public offering (IPO), marking a significant milestone in the company’s growth.
- 2006: Google acquired YouTube, the world’s largest video-sharing platform, further expanding its digital footprint.
- 2015: Google underwent corporate restructuring, establishing Alphabet Inc. as the parent company, with Sundar Pichai serving as CEO of Google.
Notable Products and Services:
- Google Search: Google’s flagship product, providing users with fast and accurate search results across a vast array of topics and information.
- Google Ads: A powerful advertising platform that allows businesses to reach their target audience through targeted advertisements on Google’s search results and partner websites.
- YouTube: The world’s largest video-sharing platform, enabling users to upload, view, and share videos on a global scale.
- Google Maps: A web mapping service offering satellite imagery, street maps, real-time traffic updates, and navigation features.
- Google Chrome: A popular web browser known for its speed, simplicity, and security features.
- Google Drive: A cloud storage and file-sharing service that allows users to store, access, and collaborate on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
- Android: An open-source mobile operating system used by millions of smartphones and devices worldwide.
Interesting Facts:
- Google derived its name from the term “googol,” which represents a one followed by a hundred zeros, symbolizing the vast amount of information the company aims to organize and make accessible.
- The Google logo features a distinctive multicolored design, representing the company’s playful and creative culture.
- Google’s headquarters, known as the Googleplex, is located in Mountain View, California and is renowned for its innovative work environment.
- Google’s corporate motto is “Don’t Be Evil,” emphasizing the company’s commitment to ethical practices and responsible use of technology.
- Google’s search engine processes billions of search queries every day, providing users with access to an extensive amount of information from around the world.
Android Operating System:

The Birth of Android:
- Andy Rubin: Andy Rubin, a renowned American computer programmer and entrepreneur, founded Android Inc. in Palo Alto, California in 2003. His vision was to develop a mobile operating system that would enable seamless and intuitive communication and computing on smartphones.
- Rich Miner: Alongside Andy Rubin, Rich Miner played a pivotal role as a co-founder of Android Inc., contributing to the strategic development and growth of the Android operating system.
Key Milestones:
- 2005: Google, recognizing the potential of Android, acquired Android Inc., forming a partnership that would shape the future of mobile technology.
- 2007: The Open Handset Alliance (OHA) was established, comprising a consortium of technology companies, including Google, HTC, Samsung, and many others. The OHA aimed to collaborate on the development and promotion of the Android platform.
- 2008: The first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream (also known as the T-Mobile G1), was released. This marked the introduction of the Android operating system to consumers, showcasing its innovative features and capabilities.
Key Features and Advancements:
- Open-Source Nature: Android’s open-source nature allows developers to access and modify its source code, fostering a vibrant ecosystem of apps and customization.
- Google Play Store: The Google Play Store provides a vast repository of applications, games, and digital content for users to download and enjoy on their Android devices.
- Widgets and Customization: Android allows users to personalize their home screens with widgets, shortcuts, and custom themes, offering a unique and tailored user experience.
- Notification Center: Android’s intuitive notification center provides users with a centralized hub to access and manage notifications from various apps and services.
- Google Assistant: The integration of Google Assistant, an AI-powered virtual assistant, enables users to interact with their devices through voice commands, accessing information, and performing tasks effortlessly.
- Android Security: Android continuously evolves its security features, including regular security updates, app sandboxing, and robust permissions management, to protect user data and ensure device security.
Dominance in the Mobile Market:
- Android’s global market share dominates the mobile industry, powering a wide range of smartphones and devices from leading manufacturers such as Samsung, Huawei, and Xiaomi.
- Android’s versatility extends beyond smartphones, with its presence in other devices such as tablets, smart TVs, wearables, and even automobiles.
Continued Innovation:
- Each version of Android is named after a dessert or sweet treat, such as Cupcake, KitKat, Marshmallow, and Pie, reflecting Google’s playful and creative approach to software development.
- Google continues to enhance the Android experience, introducing features like Android Auto for seamless integration with vehicles and Android Go for optimized performance on entry-level devices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Larry Page and Sergey Brin are the visionary inventors behind Google, the world’s leading search engine and technology giant. Their groundbreaking search algorithm, PageRank, revolutionized web indexing and provided the foundation for Google’s success. Through their innovative mindset, relentless pursuit of excellence, and commitment to organizing and making information universally accessible, Page and Brin transformed Google from a small project in a Stanford University dorm room to a global phenomenon that touches the lives of billions.
The journey of Google showcases the power of entrepreneurship, innovation, and perseverance. Page and Brin’s partnership exemplifies the importance of collaboration and complementary skills in building a successful venture. Their commitment to creating a search engine that offered accurate, relevant, and efficient results laid the groundwork for the incredible growth and influence that Google enjoys today.
From its inception as Backrub to its incorporation as Google Inc., the company has continually pushed the boundaries of technology and diversified its offerings. Google has become much more than a search engine, expanding into various sectors, including advertising (Google AdWords), video-sharing (YouTube), cloud computing (Google Cloud), and mobile operating systems (Android). These developments have solidified Google’s position as a multifaceted tech giant, constantly innovating and shaping the digital landscape.
The impact of Google goes beyond technological advancements. It has transformed how we access information, communicate, and navigate the digital world. Google’s commitment to organizing the world’s information and making it universally accessible has democratized knowledge and empowered individuals and businesses alike.
As Google continues to evolve under the umbrella of Alphabet Inc., with Sundar Pichai at the helm, it remains a symbol of innovation and technological prowess. The company’s commitment to its core values, including user-focused design, ethical practices, and continuous improvement, ensures that it stays at the forefront of the ever-changing tech industry.
In summary, Larry Page and Sergey Brin’s invention of Google revolutionized the way we search, access information, and navigate the digital landscape. Their innovative spirit and groundbreaking search algorithm, PageRank, propelled Google to become the global leader in technology. From its humble beginnings at Stanford University to its position as a multifaceted tech giant, Google’s influence continues to shape the world we live in today.
References:
- “The Google Story: From Backrub to Billion-Dollar Empire” by David A. Vise
- “In the Plex: How Google Thinks, Works, and Shapes Our Lives” by Steven Levy
- “The Search: How Google and Its Rivals Rewrote the Rules of Business and Transformed Our Culture” by John Battelle
- “Larry Page and Sergey Brin: The Founders of Google” by Matt Doeden
- “The Google Guys: Inside the Brilliant Minds of Google Founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin” by Richard L. Brandt
- “Sergey Brin and Larry Page: The Creators of Google” by Diane Dakers
- “Google: How Google Works” by Eric Schmidt and Jonathan Rosenberg
- “The Google Legacy: How Google’s Collaboration with the CIA and NSA Is Endangering Democracy” by Robert Epstein
- “Google Speaks: Secrets of the World’s Greatest Billionaire Entrepreneurs, Sergey Brin and Larry Page” by Janet Lowe
- “Inside Larry and Sergey’s Brain” by Richard L. Brandt
- “Google: A Biography” by Adam Woog
- “The Founders at Work: Stories of Startups’ Early Days” by Jessica Livingston