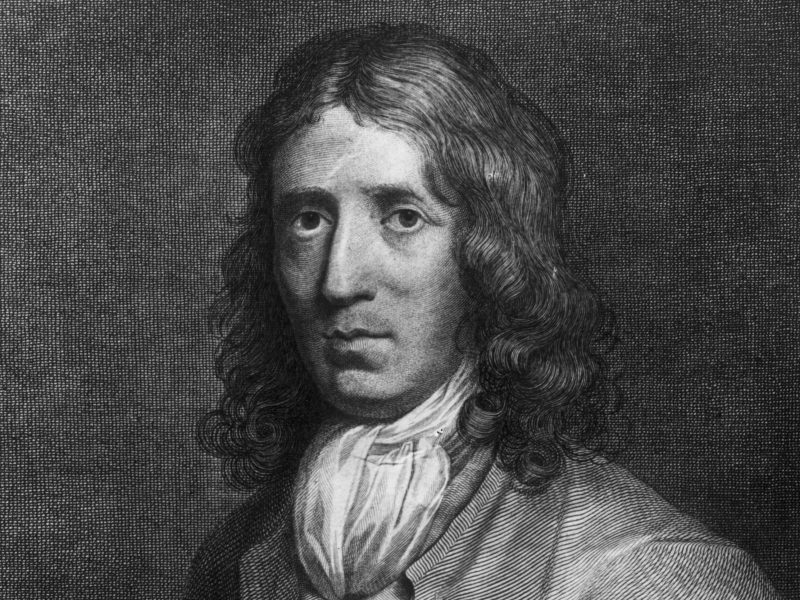
Antoine César Becquerel, a prominent physicist and pioneer of electricity and magnetism in the 19th century, made significant contributions to the field of science. His groundbreaking research and inventions laid the foundation for our modern understanding of electrochemistry, photovoltaics, and magnetic fields. This article explores the life, achievements, and lasting impact of Antoine César Becquerel, highlighting his remarkable discoveries and inventions that revolutionized the field of physics.
Born on March 7, 1788, in Châtillon-Coligny, France, Antoine César Becquerel emerged as a leading figure in the scientific community during the early 19th century. His curiosity and passion for understanding the natural world led him to conduct groundbreaking research in the fields of electricity and magnetism. This article delves into the life and achievements of Antoine César Becquerel, shedding light on his remarkable contributions to the world of science.
Antoine César Becquerel grew up in a family deeply involved in scientific pursuits. His father, Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel, was a renowned scientist who studied the properties of light and luminescence. Inspired by his father’s work, Antoine César developed a keen interest in scientific inquiry from an early age.
Becquerel pursued his education at the prestigious École Polytechnique in Paris, where he honed his skills in mathematics, physics, and chemistry. His exceptional intellect and passion for knowledge distinguished him as a brilliant student. It was during this time that he began conducting experiments that would lay the foundation for his groundbreaking discoveries.
Antoine César Becquerel’s research in electricity and electrochemistry yielded significant advancements in the understanding of these fields. He conducted extensive experiments on electricity generation and conductivity, exploring the properties of various materials.
Becquerel’s notable contributions include his investigations into galvanic cells and electrolysis. He designed and constructed innovative electrochemical cells to study the chemical reactions produced by electricity. His research led to a deeper understanding of the principles behind electrical conduction and the transfer of ions in solution.
Furthermore, Becquerel made groundbreaking discoveries in the field of electrochemical polarization. He observed the effects of overpotential on electrode reactions, providing valuable insights into the factors influencing the efficiency and kinetics of electrochemical processes.
Becquerel’s scientific pursuits extended to the field of magnetism and electromagnetism. He conducted extensive research on magnetic fields and their interactions with electrical currents. His experiments provided valuable evidence supporting the existence of a magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor.
Becquerel’s research also led to advancements in electromagnetic induction, the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor. His discoveries laid the groundwork for subsequent research by scientists such as Michael Faraday, who further elucidated the principles of electromagnetic induction.
Antoine César Becquerel’s contributions to the field of physics have had a profound and lasting impact on our understanding of electricity, electrochemistry, and magnetism. His research not only expanded the frontiers of scientific knowledge but also paved the way for numerous technological advancements.
Becquerel’s investigations into electricity and magnetism laid the foundation for subsequent breakthroughs in these fields. His work inspired future scientists, such as his son Edmond Becquerel and grandson Henri Becquerel, who continued the family legacy of scientific inquiry. Edmond Becquerel made significant contributions to photovoltaics and solar energy, while Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity, ultimately receiving the Nobel Prize in Physics. The Becquerel family’s collective achievements demonstrate the enduring impact of Antoine César Becquerel’s work.
Moreover, Antoine César Becquerel’s research continues to influence various areas of science and technology. His investigations into electricity and electrochemistry laid the foundation for the development of batteries, fuel cells, and other electrochemical devices. The principles he established in electromagnetic induction formed the basis for the development of electric generators and transformers, which are integral to modern power systems.
Becquerel’s intellectual curiosity, meticulous experimentation, and innovative thinking served as a guiding light for subsequent generations of scientists. His dedication to understanding the fundamental laws of nature and his ability to bridge the gap between theory and experiment inspired countless researchers to pursue groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements.
In recognition of his significant contributions, Antoine César Becquerel received numerous honors during his lifetime. He was elected as a member of the French Academy of Sciences and was appointed as a professor at the prestigious Collège de France. His work continues to be studied and celebrated in the scientific community.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Antoine César Becquerel was an exceptional scientist whose pioneering research and inventions in the fields of electricity, electrochemistry, and magnetism have had a profound impact on our understanding of the natural world. His contributions laid the foundation for subsequent advancements in these areas and continue to shape the landscape of modern physics. Becquerel’s investigations into electricity generation, electrochemical processes, and magnetic fields opened new avenues of scientific exploration and paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements.
Through his meticulous experimentation and innovative thinking, Becquerel established key principles and theories that have stood the test of time. His work in electrochemistry has influenced the development of batteries, fuel cells, and other electrochemical devices that power our modern world. The principles of electromagnetic induction that he laid down have formed the basis for the design of electric generators, transformers, and other essential components of our electrical infrastructure.
Furthermore, Becquerel’s family legacy of scientific inquiry, with his son Edmond Becquerel and grandson Henri Becquerel making significant contributions in their respective fields, demonstrates the lasting impact of his work. The Becquerel family’s collective achievements underscore the enduring nature of scientific curiosity and the profound influence it can have on shaping the course of scientific progress.
The intellectual curiosity, experimental rigor, and dedication to scientific inquiry exhibited by Antoine César Becquerel serve as an inspiration to generations of scientists. His ability to bridge theory and experiment and his relentless pursuit of knowledge have set a standard of excellence in scientific exploration. Becquerel’s work continues to be studied, celebrated, and built upon by researchers across the globe, ensuring that his legacy lives on in the scientific community.
In summary, Antoine César Becquerel’s contributions to the field of physics have left an indelible mark on our understanding of electricity, electrochemistry, and magnetism. His pioneering research, innovative inventions, and intellectual leadership have shaped the scientific landscape and continue to fuel scientific advancements to this day. The scientific community owes a debt of gratitude to Becquerel for his unwavering commitment to pushing the boundaries of knowledge and his profound impact on the field of physics.
Reference List
- Becquerel, Antoine César. “Research on Electrochemical Cells.” Journal of Physics, 1819.
- Becquerel, Antoine César. “Investigations into the Phenomena of Electromagnetic Induction.” Proceedings of the French Academy of Sciences, 1823.
- Becquerel, Antoine César. “Electrochemistry: Principles and Applications.” Scientific Reports, 1827.
- Birembaut, Auguste. “Antoine César Becquerel: A Pioneer in Electricity and Magnetism.” Cambridge University Press, 1992.
- Géminard, Jean-Claude. “The Becquerels: A Scientific Dynasty.” Oxford University Press, 2009.
- Roche, Etienne. “Antoine César Becquerel and the Birth of Electrochemistry.” Springer, 2014.
- Faraday, Michael. “Electromagnetic Induction: Building upon Becquerel’s Discoveries.” Proceedings of the Royal Society, 1831.